There are compelling reasons for attorneys to draft in the manner that they do, and it is a talent that is developed with time. We will cover the following topics in this blog:
- What are the fundamental contract drafting principles?
- What are some pointers on how to write a good contract?
As a legal expert, one of the most crucial skills you must have is contract drafting. It is the single most crucial skill that will be demanded of you when you enter the profession, whether in a legal firm or as in-house counsel, even as a law student.
The pre-requisite here is that you need to have appropriate knowledge of the Indian Contract Act and relevant add on laws that are incidental to your subject matter. For example: If I am drafting a contract for a partnership firm , I have to keep in mind the relevant laws applicable to partnership firms, like the Indian Partnership Act or the Limited liability partnership Act along with the contract law rules and procedure. This blog does not deal with these issues.
> Did you know you can send a legal notice online for as low as Rs. 599?
Basic 101 of Contract Drafting for Beginners lays down certain principles that you should follow while drafting your contracts and agreements.
Table of Contents
Using Correct Language
Language is of the essence. And because Indians are not natural English speakers, they may frequently use the language incorrectly. As a result, the courts may not consider the text’s literal meaning. But that should not be an excuse for drafting poor contracts. The use of correct punctuations, active voices (most of the times) and not missing out on the grammar or the styles are a must during the course of drafting.
Read: How using Correct Language is an essential for contract drafting?
Pre-Contractual Instruments
When two parties decide to enter into a contract, there may have been some informal interaction. For example, they show their respective interests or an intention to negotiate prior to a formal binding contract. These could be recorded in what are called as pre-contractual instruments. Examples of such instruments includes: term sheets, letters of intent, letters of award, and even memorandum of understanding.
Each of these pre-contractual instruments play an essential role in contract drafting.
Read: What are pre-contractual instruments?
Introductory parts of an agreement.
These introductory parts may consist of the title of the agreement, the date and the place of execution of the agreement, and the recitals.
Title of the Agreement
A title is one of the important parts of an agreement. Some examples of titles are:
- “Agreement for Catering Services”
- “Sale and Purchase Agreement”
- “Lease Deed”
- “Leave and License Agreement”
- “Indemnity Agreement“
While the title could simply be “agreement”, often this name giving is for the fancy.
Date of the agreement
The date on which the parties signed the agreement is known as the agreement’s date. In most cases, the parties sign the contract on the same day. There are, nevertheless, circumstances in which the parties may execute the agreement on separate dates.
What happens when parties want an agreement to have retrospective effect? That is, effect from a period prior to the signing of the agreement. To do that, you could simply add an “Effective Date”. Such a clause could look like this: “An agreement shall be effective from so and so date.” or “The effective date of the agreement shall be so and so date.”
Place of execution
The place of execution of the agreement, that is, the place where the document is signed by the parties, is usually provided at the beginning of the agreement. A typical clause says: “This agreement executed at Mumbai on the 4th October 2018… .” The place of execution has important implications because the court at the place of execution can have jurisdiction over a dispute.
Recitals
What is the meaning of the term ‘Recitals” in agreements and contracts?
Recitals are the introductory terms which give an idea of how the agreement came to be. In other words they provide the background and essence of the story behind the agreement. It basically mentions the crux of the party’s discussions. This section is usually present just before the body of the agreement and it may be titles, “Whereas”, or “Preamble” or simple “Recital Clause”.
Recitals could be of several types including but not limited to party related recitals, background related recitals. It is a section that you could say defines the agreement or contract in non-legal terms.
Definition and Interpretation clause
Just like the statutes and other provisions of law, agreements also need its words to be defined in a way that it could be interpreted in a particular way. It is important to define words in the definition section that you think could otherwise be vaguely interpreted or incorrectly interpreted. Also, while drafting the definition clause one must take into account the use of words like “means”, “includes”, “& other”.
The Interpretation clauses may also include conflict provisions that explain and provides remedy in situations where there is a conflict or even a possible conflict. For example: Clauses like “In case of any conflict of provision the last agreement in place shall prevail.” could very well be used.
Tools like “Entire Agreement clause” also plays a pivotal role in the interpretation section.
“This contract supersedes all prior agreement and understandings, whether oral or written, in connection therewith.”
Example
The above ‘entire agreement clause’ could be used to put a blanket ban on all of the previous conversation and agreement that took place earlier between the parties.
Read: Secrets of drafting the Definition and Interpretation clause!
Severability clause
It may sometimes happen that a particular act as promised in the agreement cannot be performed by either of the parties because of reasons not connected with them or for reasons that they have no control over. In other words, if there’s an act that was promised to be performed cannot be performed for some reason. Then such a clause can be severed (or parted with) without affecting the whole contract. It is important to mention how such severability will take place.
Any part, provision, representation or warranty of this Agreement which is prohibited or which is held to be void or unenforceable shall be ineffective to the extent of such prohibition or unenforceability without invalidating the remaining provisions hereof.
Example
No waiver clause
What is a ‘no waiver clause’?
Suppose you have agreed to perform a particular act on or before the 5th of every month for the entire duration of the agreement. In one instance, you have delayed in performing that act by the due date. Unless time is of the essence in that agreement and the other party has accepted your delay in performance. The use of the no waiver clause here basically abstains you from delaying future performances just because your first delay was allowed by the other party.
“A party’s failure to perform any clause or implement any rights under the agreement at any time shall not impair the party’s right to request performance, nor shall any party’s waiver of a violation be considered a waiver of any subsequent breach.”.
Example
> Read: How do draft a no waiver clause?
Performance clause
This clause lays down the procedure on the promise under the agreement is to be performed. It could lay strict guidelines or a basic framework within which the promise must be performed by the parties.
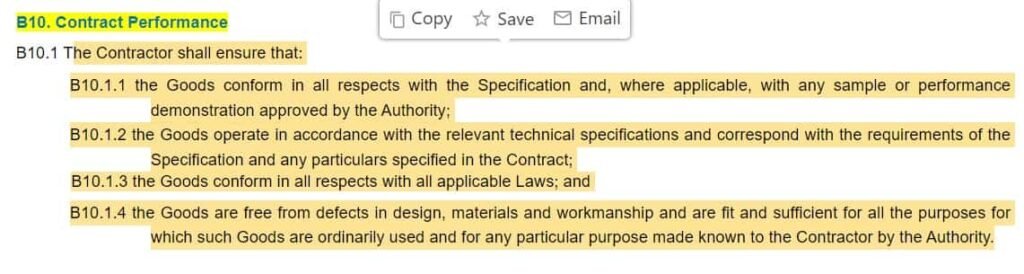
>Read: Essentials of drafting a performance clause in agreements
Other Clauses
There could be an endless list of clauses depending on the type and requirement of the agreement including but not limited to:
Representation & Warranties
Representation and warranties or popularly understood by the terms “Conditions and Warranties”. The Indian Contract act specifies that Stipulations that are essential to the main purpose or the crux of the agreement are known as conditions. These bare basic conditions are necessary to meet for the performance of the contract, if not, the aggrieved party can repudiate the contract and claim damages.
Warranties on the other hand are collateral to the main purpose of the contract. The breach of which may entitle the aggrieved party to claim damages but not to repudiate the contract.
A typical contract must ensure that it has laid down clearly the conditions and warranties so as to avoid clashes in the future.
Time clause
“Time is of the essence” is usually used in agreements to denote that time plays a pivotal role in performance of the contract/agreement.
Both the parties agrees that, with respect to each and every obligation and covenant contained in this Agreement and the other Documents contained herewith, time is of the essence.
Example
Force majeure Clause
This clause should be used in all types of agreements. Force majeure clauses absolves the parties from performing the contract in case of supervening impossibility. Suppose, If A has promised to deliver certain goods by a certain date to B and he is unable to do so because of some reason. He can absolve himself from performing the obligation by compensating the damages caused to B as per the force majeure clause in their agreement.
In no event shall the parties be responsible or liable for any failure or delay in the performance of its obligations hereunder arising out of or caused by, directly or indirectly, forces beyond its control, including, without limitation, strikes, work stoppages, accidents, acts of war or terrorism.
Example
Intellectual Property Clause
This section shall include ways, procedure and limitations of assigning and use of intellectual property obtained under the agreement. In an agreement for employment of a content writer, the IP clause could include who shall have the right to own the content produced during the course of employment and it what way it will be licensed.
Read: Intellectual Property Ownership
Assignment Clause
An assignment clause simply lays down rules regarding the party’s ability to assign the work or the performance of the contract to some third party or outsider. It may include a provision so as to bar assignment totally or to seek authorization before assignment.
Any attempt to assign (directly or indirectly) this agreement to a third party or an outsider, without prior written consent of the contractor shall be void from the beginning.
Example that bars assignment.
Remedies for contractual breach
Agreements are meeting of minds and as far as we know of human mind, they tend to change at times. There will always be a possibility that one of the parties breaches the contract. What do we do then?
We should go back in time and insert “remedies for contractual breach clause”.
This clause lays down the possible ways to deal situations in case either or both the parties breaches the contract or agreement.
This section typically contains three subsections:
- Contractual breach: Further sub-divided into de minimis breaches, material breaches and non-material breaches.
- Suspension clause: How long can the agreement be suspended?
- Termination clause: If the contract can be terminated and in what way?
Confidentiality clause
Confidentiality or non-disclosure clause as it is popularly known in India is of great importance when the agreement includes exchange of substantial amount of information, the leak of which could bring enormous amount of trouble to either or both the parties. Confidentiality clauses are used not only in employment agreements but also in a variety of agreements.
Dispute Resolution
Last but not the least, an agreement must take into consideration how it plans to deal with disputes. This clause can lay down the process and procedure to appoint arbitrator or to decide a specific jurisdiction for arbitration or certain other measures for dispute resolutions.
All or any disputes arising out or touching upon or in relation to the terms and conditions of this Agreement, including the interpretation and validity of the terms thereof and the respective rights and obligations of the Parties, shall be settled amicably by mutual discussion, failing which the same shall be settled through arbitration at the appropriate forum within the jurisdiction of India
Example
Conclusion
These are the few basics of Contract drafting essentials. The details of each clauses have been dealt with at the end of their respective paragraphs. Please use the hyperlink to read more and view their practical uses.

Passionate about using the law to make a difference in people’s lives. An Advocate by profession.




